The Challenge
"How do we recover valuable galactic data without spending millions on additional telescope time?"
Observational astronomy faces a critical bottleneck: low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) renders distant galaxy images nearly unusable. Traditional solutions require expensive re-observation campaigns. This research explores whether deep learning can recover what's already there.
Live Demo

Real-time denoising: Watch the model progressively refine a galaxy image from noise to structure
Two Approaches, One Goal
Architecture A: Residual Attention U-Net
Input: Noisy Galaxy Image (SNR < 5)
↓
[Encoder] → [Spatial Attention] → [Skip Connections]
↓
[Decoder] with Residual Refinement
↓
Output: Enhanced Galaxy Image
Key innovations:
- Residual connections preserve gradient flow through 12+ layers
- Spatial attention gates focus compute on galactic regions
- Direct pixel-to-pixel translation in single forward pass
Architecture B: Guided Diffusion Model (DDPM)
Forward Process: Reverse Process:
Galaxy → Noise (T steps) Noise → Galaxy (T steps)
↓ ↑
Learned noise schedule Learned denoising network
↓ ↑
Condition on: SNR level Probabilistic sampling
Why diffusion wins:
- Probabilistic outputs = uncertainty quantification per pixel
- Iterative refinement = gradual structure emergence
- Conditioning mechanisms = control over generation process
The Results
Quantitative Improvements
Metric Low-SNR U-Net DDPM Gain
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
PSNR ~12 dB ~28 dB ~32 dB +4 dB
SSIM 0.35 0.82 0.91 +0.09
Structure Preservation Baseline Good Excellent —
Visual Evidence
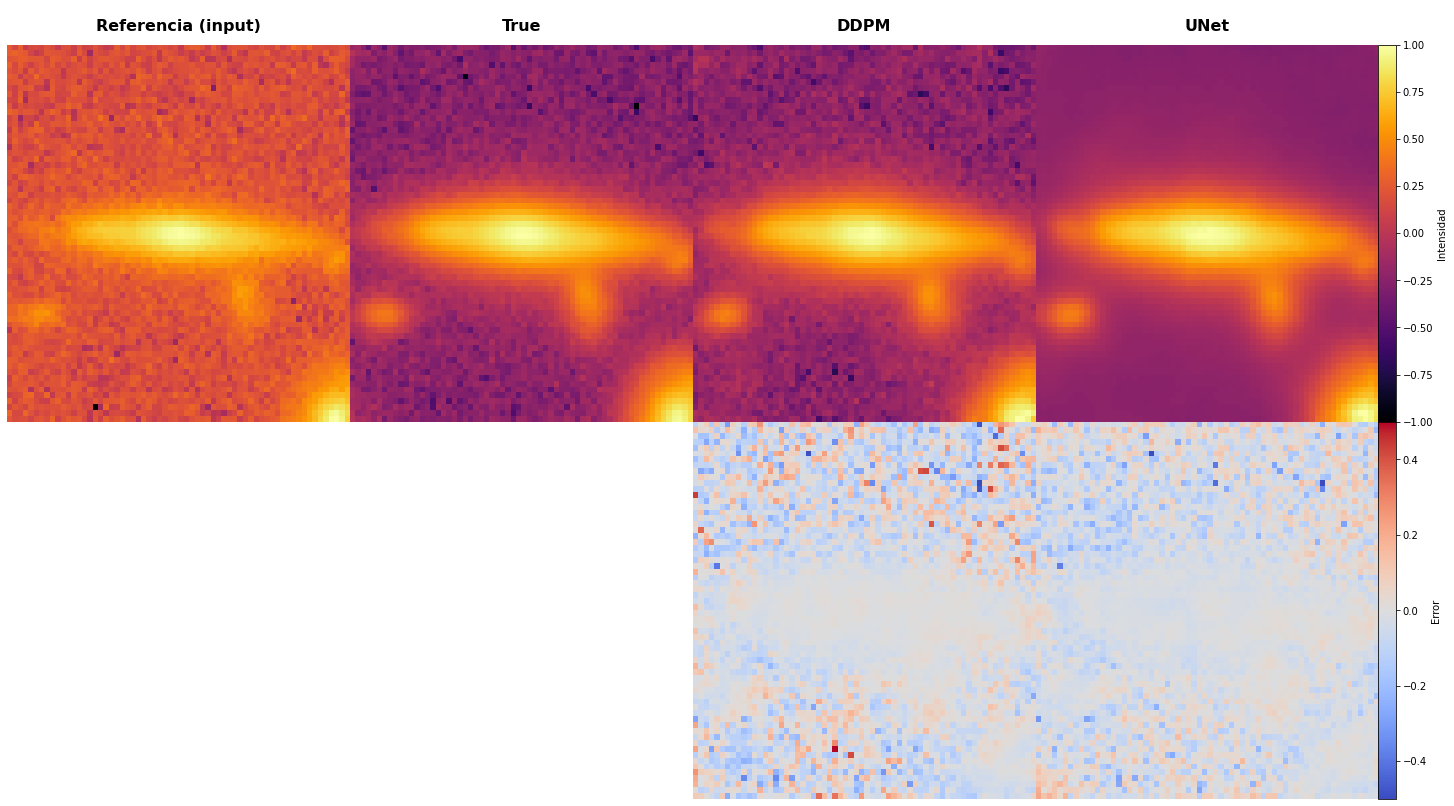
Case Study 1: Spiral Galaxy Recovery
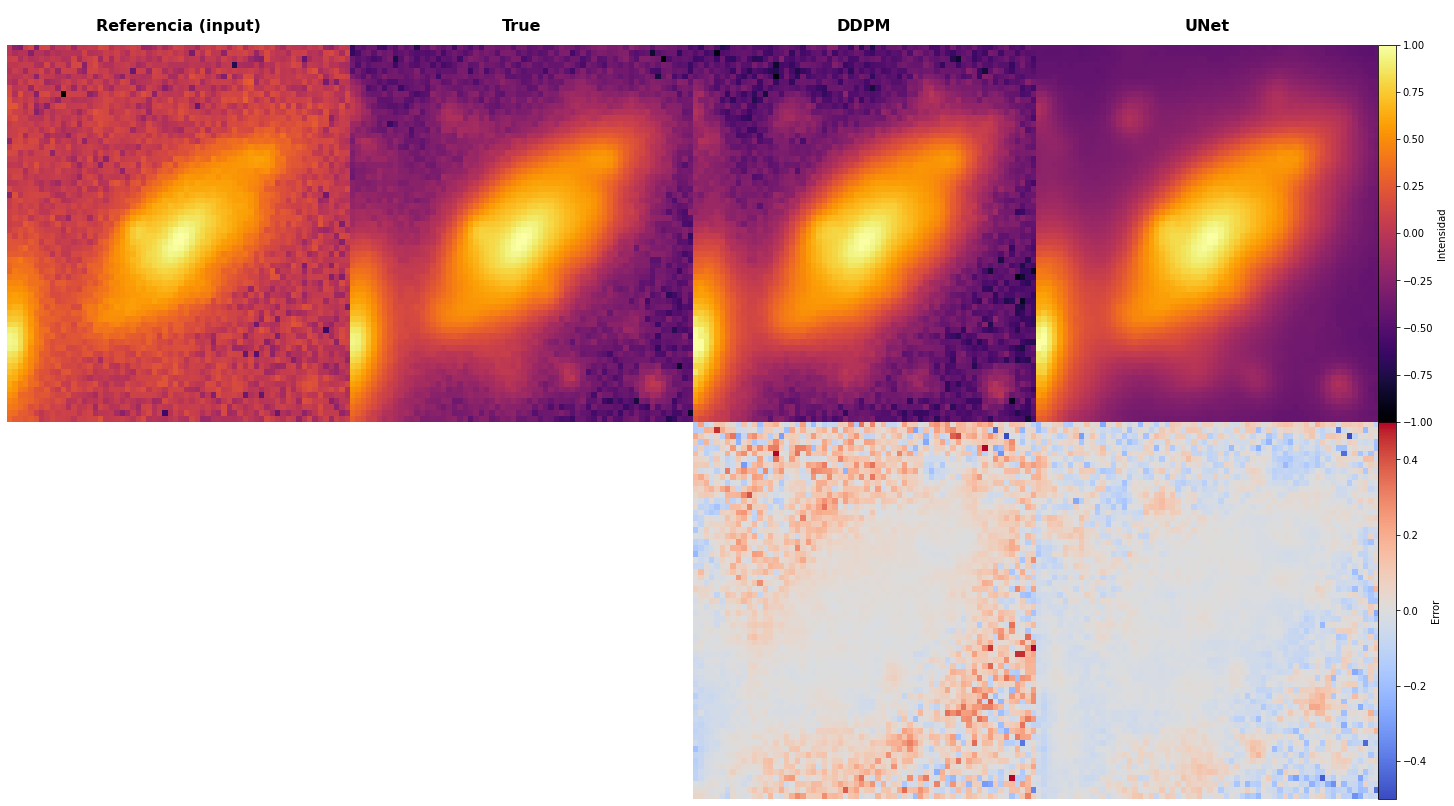
Case Study 2: Irregular Galaxy Structure
Case Study 3: Edge-on Galaxy Detail Recovery
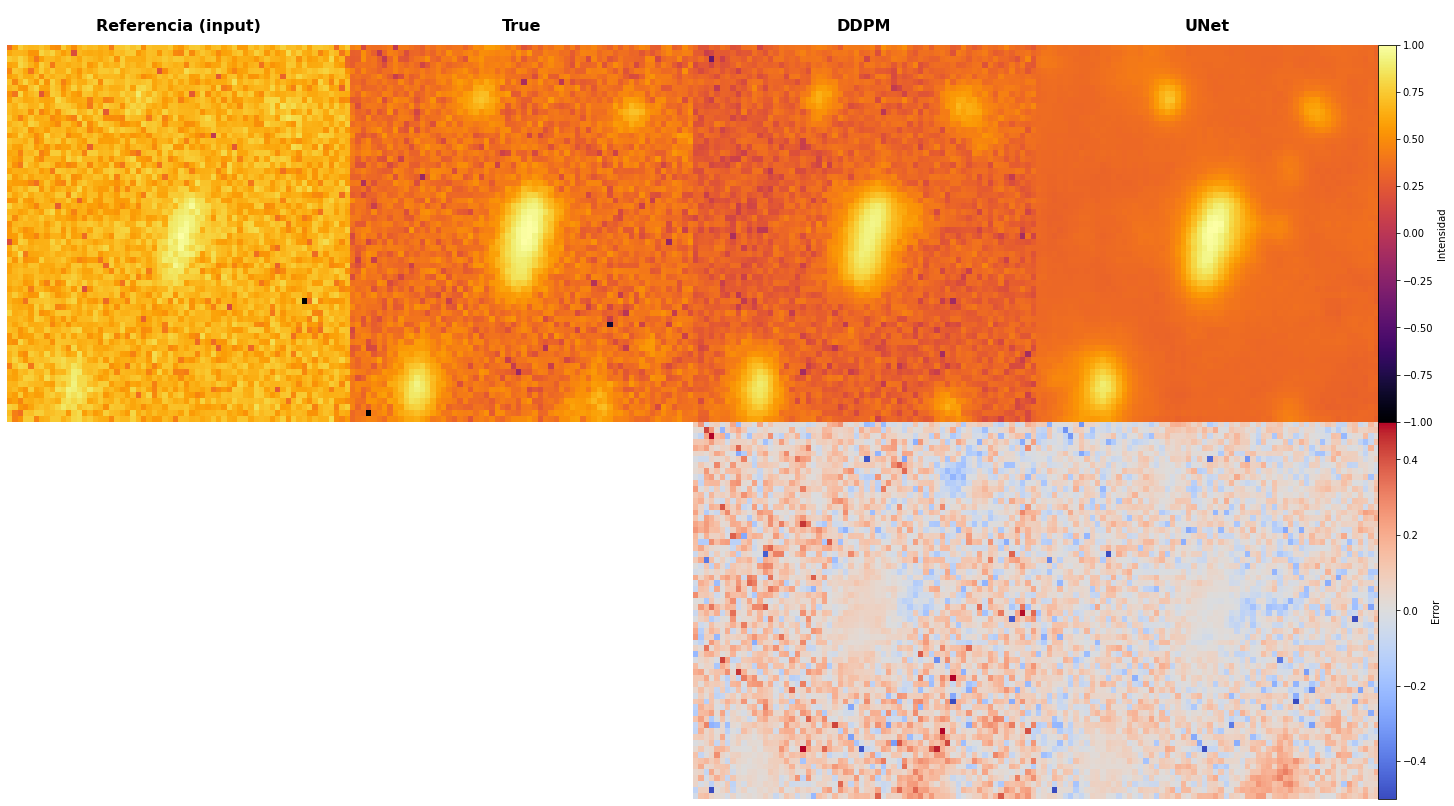
Key Insight: DDPM excels at preserving fine structural details that U-Net smooths over—critical for astrophysical analysis.
Technical Implementation
Stack
Framework: PyTorch Lightning 2.0
Compute: Distributed GPU training (4x A100)
Data Pipeline:
- Format: FITS (Flexible Image Transport System)
- Preprocessing: Custom SNR estimation & normalization
- Augmentation: Rotation, flip, intensity scaling
Training:
- Duration: ~72 hours
- Samples: 50,000+ galaxy patches
- Checkpointing: Every 5 epochs with validation
Architecture Highlights
RAUNet:
- 4-level encoder-decoder with skip connections
- Squeeze-and-Excitation attention modules
- Instance normalization for batch stability
DDPM:
- 1000-step diffusion schedule (cosine β)
- U-Net backbone with time embedding
- Classifier-free guidance for controllable generation
Research Impact
This work demonstrates that generative models can surpass discriminative approaches in scientific imaging tasks where uncertainty matters. The probabilistic nature of diffusion models provides astronomers with confidence intervals—essential for drawing conclusions about distant galaxies.
Master's Thesis — 2024